The following murmurs are heard in the aortic area: Pulmonic area overlies the fourth and fifth thoracic vertebrae and the corresponding interspaces to the left and right of the spine. Likewise, a gallop rhythm, the result of a loud S3 and S4, and tachycardia are abnormal. The volume overload of blood in the left atrium and left ventricle lead to increased pulmonary venous engorgement. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. It is especially good for hearing the mitral insufficiency murmur. The rise in the oxygen tension of the blood bathing the ductus may also contribute to ductal constriction.  It is the duty of a judge to give an opinion on every point of law, properly arising out of the issue, which is The most common cause of hyperthermia in the newborn is. The infant presents with progressive cyanosis, pallor, and mottling. The reported sensitivity for detection of a pathologic heart murmur in newborns ranges from 80.5 to 94.9 percent among pediatric cardiologists, with specificity ranging from 25 to 92 percent.32,43 These variations are significant because the lowest specificity corresponds to positive and negative LRs of 1.1 and 0.7, which are uninformative, and the highest specificity corresponds to positive and negative LRs of 10 and 0.21, which are quite accurate. This means that a catheter can be passed from the right to the left atrium during cardiac catheterization, or that probe can be passed through the foramen ovale during cardiovascular surgery.
It is the duty of a judge to give an opinion on every point of law, properly arising out of the issue, which is The most common cause of hyperthermia in the newborn is. The infant presents with progressive cyanosis, pallor, and mottling. The reported sensitivity for detection of a pathologic heart murmur in newborns ranges from 80.5 to 94.9 percent among pediatric cardiologists, with specificity ranging from 25 to 92 percent.32,43 These variations are significant because the lowest specificity corresponds to positive and negative LRs of 1.1 and 0.7, which are uninformative, and the highest specificity corresponds to positive and negative LRs of 10 and 0.21, which are quite accurate. This means that a catheter can be passed from the right to the left atrium during cardiac catheterization, or that probe can be passed through the foramen ovale during cardiovascular surgery.  There will be loud harsh systolic murmur. Signs of shock can be observed with abnormal skin perfusion when capillary refill is > 3 seconds, prolonged in lower body compared with upper body and mottling associated with other symptoms. Cardiomegaly is present with CHF. Expert auscultation of the neonatal heart requires much practice over time. It may be missed because it is often very soft or may be mistaken for breath sounds because of its high pitch. 21(3) 31 36. The clamping of the umbilical cord and the subsequent removal of the placenta causes immediate circulatory changes in the neonate.
There will be loud harsh systolic murmur. Signs of shock can be observed with abnormal skin perfusion when capillary refill is > 3 seconds, prolonged in lower body compared with upper body and mottling associated with other symptoms. Cardiomegaly is present with CHF. Expert auscultation of the neonatal heart requires much practice over time. It may be missed because it is often very soft or may be mistaken for breath sounds because of its high pitch. 21(3) 31 36. The clamping of the umbilical cord and the subsequent removal of the placenta causes immediate circulatory changes in the neonate.
The three major fetal shunts, the ductus venosus, the foramen ovale and the patent ductus arteriosus are normally eliminated within the first days of life. The size of the defect and the degree of pulmonary vascular resistance are more important to severity than location. Left Ventricular Area centered around the apex of the heart. Surgical correction is accomplished by a simple patch or with direct closure. Chronic arterial desaturation stimulates erythropoiesis, causing polycythemia that may lead to increased blood viscosity, microcytic anemia, and cerebrovascular accident. There is increased blood flow to the right ventricle through the pulmonary valve. Its onset is 12 to 24 hours. The following sounds are best heard over the pulmonary area: Murmurs caused by increased flow of the pulmonary artery, The pulmonary component of the second heart sound. to help console her infant? Wide splitting of S1 is heard in a newborn with right bundle branch block or Epsteins anomaly. More common in children with a first-degree relative who has CHD (three- to 10-fold increased risk, Sudden cardiac death or hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, Increased risk of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (autosomal dominant pattern), Can be secondary to undiagnosed CHD lesions, Certain genetic disorders (e.g., DiGeorge syndrome, velo-cardio-facial syndrome) are associated with cardiac malformations, Aneuploidy (e.g., trisomy 21, Turner syndrome), Trisomy 21 is associated with an increased risk of atrioventricular septal defects, atrial septal defects, ventricular septal defects, patent ductus arteriosus, and tetralogy of Fallot, Connective tissue disorder (e.g., Marfan syndrome), Turner syndrome is associated with increased risk of coarctation of the aorta, aortic valve stenosis, and left ventricular hypertrophy, Marfan syndrome is associated with mitral valve prolapse, aortic root dilation, and aortic insufficiency, Major congenital defects of other organ systems, Respiratory symptoms may be attributable to heart disease (i.e., congestive heart failure); enlarged vessels may lead to atelectasis or difficulty clearing respiratory secretions, thereby promoting infection, Leading cause of acquired cardiac disease in children; can cause coronary artery aneurysm and stenosis, Associated with development of rheumatic heart disease, In utero exposure to alcohol or other toxins, Fetal alcohol syndrome is associated with an increased risk of atrial and ventricular septal defects, and tetralogy of Fallot, In utero exposure to selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors or other potentially teratogenic medications, Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor exposure is associated with a small but statistically significant increased risk of mild heart lesions, including ventricular septal defects and bicuspid aortic valve (although not all studies found an increased risk, Lithium exposure is associated with Ebstein anomaly of the tricuspid valve, Valproate (Depacon) exposure is associated with coarctation of the aorta and hypoplastic left heart syndrome, Maternal infections may increase risk of structural heart lesions (e.g., maternal rubella infection is associated with patent ductus arteriosus and peripheral pulmonary stenosis), Increased risk of CHD, including transient hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, tetralogy of Fallot, truncus arteriosus, and double-outlet right ventricle, CHD is associated with other conditions (e.g., genetic disorders, in utero exposure to toxins) that can result in preterm birth; 50 percent of newborns weighing less than 3 lb, 5 oz (1,500 g) at birth have CHD (most commonly patent ductus arteriosus), May be related to aortic stenosis or hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, Structural heart lesion with restricted pulmonary blood flow, Multiple potential causes, including hypoxia and CHF, May be related to arrhythmias secondary to structural heart lesions, Congenital heart lesions are more common in children with certain genetic disorders and syndromes, May indicate CHF, hypoxia, or poor cardiac fitness, Poor exercise tolerance or capacity for play, May indicate CHF, poor cardiac fitness, or a genetic disorder or syndrome; poor weight gain most commonly reflects decreased cardiac output or left-to-right shunts with pulmonary hypertension, Cardiac asthma resulting from pulmonary congestion, Atelectasis or difficulty clearing secretions because of pulmonary vascular congestion, Abnormal growth (height and weight plotted on growth chart), Feeding difficulties may be a sign of cardiac disease in newborns and infants (decreased exercise capacity), Certain genetic disorders may increase risk of delayed growth and CHD, Abnormal vital signs (compared with age-adjusted norms), Arrhythmia, tachycardia, hypoxia, and tachypnea may indicate underlying structural heart disease, Blood pressure discrepancy between upper and lower limbs may indicate coarctation of the aorta (pressure gradient of > 20 mm Hg with low blood pressure in the lower extremities), Adventitial breath sounds (e.g., wheezing, rales, ronchi, pleural rub), Wheezing may be associated with cardiac asthma; rales may be associated with pulmonary congestion secondary to congestive heart failure, Chest contour signaling maldevelopment of the sternum, Defective segmentation of the sternum may occur in children with CHD, Certain genetic or congenital conditions increase risk of CHD, Normal peripheral perfusion is less than 2 to 3 seconds; delay may indicate poor perfusion secondary to diminished cardiac output, Displaced point of maximal impulse; precordial impulses (heaves, lifts, thrills), Possible structural abnormality or ventricular enlargement, Location of liver signals abdominal situs, Systolic ejection murmur best heard over the aortic valve, High-pitched systolic murmur that can extend into diastole; best heard along the anterior chest wall over the breast, Arteriovenous anastomoses or patent ductus arteriosus, Grade 1 or 2, low-pitched, early- to mid-systolic ejection murmur heard over axilla or back, Pulmonary artery stenosis or normal breath sounds, Grade 2 or 3, crescendo-decrescendo, early- to mid-systolic murmur peaking in mid-systole; best heard at the left sternal border between the second and third intercostal spaces; characterized by a rough, dissonant quality; loudest when patient is supine and decreases when patient is upright and holding breath, Atrial septal defect or pulmonary valve stenosis, Grade 1 to 3, early systolic murmur; low to medium pitch with a vibratory or musical quality; best heard at lower left sternal border; loudest when patient is supine and decreases when patient stands, Infancy to adolescence, often 2 to 6 years, Ventricular septal defect or hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, Supraclavicular\brachiocephalic systolic murmur, Brief, low-pitched, crescendo-decrescendo murmur heard in the first two-thirds of systole; best heard above clavicles; radiates to neck; diminishes when patient hyperextends shoulders, Bicuspid/stenotic aortic valve, pulmonary valve stenosis, or coarctation of the aorta, Grade 1 to 6 continuous murmur; accentuated in diastole; has a whining, roaring, or whirring quality; best heard over low anterior neck, lateral to the sternocleinomastoid; louder on right; resolves or changes when patient is supine, Cervical arteriovenous fistulas or patent ductus arteriosus, Small defects: loud holosystolic murmur at LLSB (may not last throughout systole if defect is very small), Medium or large defects: CHF, symptoms of bronchial obstruction, frequent respiratory infections, Medium and large defects: increased right-to-left ventricular impulses; thrill at LLSB; split or loud single S, Usually asymptomatic and incidentally found on physical examination or echocardiography; large defects can be present in infants with CHF, Grade 2 or 3 systolic ejection murmur best heard at ULSB; wide split fixed S, May be asymptomatic; can cause easy fatigue, CHF, and respiratory symptoms, Continuous murmur (grade 1 to 5) in ULSB (crescendo in systole and decrescendo into diastole); normal S, Onset depends on severity of pulmonary stenosis; cyanosis may appear in infancy (2 to 6 months of age) or in childhood; other symptoms include hypercyanotic spells or decreased exercise tolerance, Central cyanosis; clubbing of nail beds; grade 3 or 4 long systolic ejection murmur heard at ULSB; may have holosystolic murmur at LLSB; systolic thrill at ULSB; normal to slightly increased S, Usually asymptomatic but may have symptoms secondary to pulmonary congestion, Systolic ejection murmur (grade 2 to 5); heard best at ULSB radiating to infraclavicular regions, axillae, and back; normal or loud S, Newborns and infants may present with CHF; older children are usually asymptomatic or may have leg pain or weakness, Systolic ejection murmur best heard over interscapular region; normal S, Usually asymptomatic; symptoms may include dyspnea, easy fatigue, chest pain, or syncope; newborns and infants may present with CHF, Systolic ejection murmur (grade 2 to 5) best heard at upper right sternal border with radiation to carotid arteries; left ventricular heave; thrill at ULSB or suprasternal notch, Variable presentation depending on type; may include cyanosis or CHF in first week of life, Cyanosis; clubbing of nail beds; single S, Total anomalous pulmonary venous connection, Grade 2 or 3 systolic ejection murmur at ULSB; grade 1 or 2 mid-diastolic flow rumble at LLSB; wide split fixed S, Early-onset cyanosis or CHF within the first month of life, Cyanosis; clubbing of nail beds; normal pulses; single S, May be asymptomatic at birth, with cyanosis and CHF developing with duct closure, Onset of CHF in first few weeks of life; minimal cyanosis, Increased cardiac impulses; holosystolic murmur (ventricular septal defect); mid-diastolic rumble, Sensitive (changes with child's position or with respiration), Small (murmur limited to a small area and nonradiating), Systolic (occurs during and is limited to systole), Johns Hopkins University Cardiac Auscultatory Recording Database, Web site: http://www.murmurlab.com/card6/ (registrationrequired), University of Michigan Heart Sound and Murmur Library, University of Washington Department of Medicine. It produces vasodilatation, smooth muscle relaxation of ductus arteriosus, and pulmonary and systematic circulations. The fetal circulatory system is supported by the placenta.  Cyanosis may be present depending on the amount of pulmonary blood flow. Symptoms result from increased pulmonary blood flow caused by the abnormal connection between both ventricles and the atria. Most newborns will pass meconium within the first, A pink macular lesion that blanches with pressure and darkens with crying and oftentimes found over the brow or on the neck is called, *Wrong: erythema toxicum & melanocytic nevus, Francesca is a 34-year-old primipara with a history of type-I diabetes. leaving the cord exposed to air and observing for redness, drainage, and/or odor.
Cyanosis may be present depending on the amount of pulmonary blood flow. Symptoms result from increased pulmonary blood flow caused by the abnormal connection between both ventricles and the atria. Most newborns will pass meconium within the first, A pink macular lesion that blanches with pressure and darkens with crying and oftentimes found over the brow or on the neck is called, *Wrong: erythema toxicum & melanocytic nevus, Francesca is a 34-year-old primipara with a history of type-I diabetes. leaving the cord exposed to air and observing for redness, drainage, and/or odor.
Structural heart disease is more likely when the murmur is holosystolic, diastolic, grade 3 or higher, or associated with a systolic click; when it increases in intensity with standing; or when it has a harsh quality. 
Diuretics Diuretics are used in the treatment of CHF to decrease fluid overload and fluid retention: Inotropic Agents These are used to increase myocardial performance by increasing the strength of contraction of the heart muscle. With aortic regurgitation the murmur is high pitched and blowing. Cases of severe valvular insufficiency, such as aortic or mitral insufficiency. The persistence of the ductus arteriosus is beyond 24 hours. Treatment is focused at preventing CHF and hypoxemia. She presented as floppy and apneic, and required bag/mask ventilation and fluid resuscitation in the delivery room. 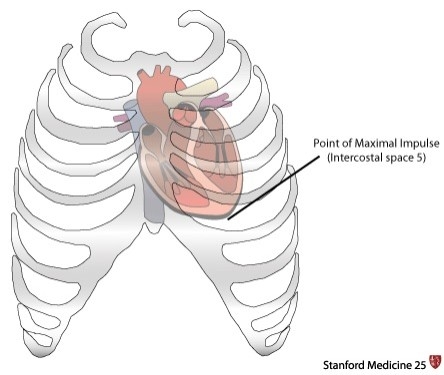 & Applewhite; (2005) Protocols in Neonatal Nursing. A soft systolic murmur is heard at the upper left sternal border. Cord occlusion causes a prompt rise in blood pressure and a corresponding stimulation of the aortic baroreceptors and the sympathetic nervous system. The definitive surgical correction is performed during infancy. A study in Oman found that the prevalence of abnormal findings on echocardiography was not significantly different between patients referred by pediatric cardiologists and those referred by primary care physicians.37 However, pediatric cardiologists more accurately detect structural heart lesions in newborns and children with heart murmurs,32,38 and can assist family physicians in the assessment of a suspicious murmur.
& Applewhite; (2005) Protocols in Neonatal Nursing. A soft systolic murmur is heard at the upper left sternal border. Cord occlusion causes a prompt rise in blood pressure and a corresponding stimulation of the aortic baroreceptors and the sympathetic nervous system. The definitive surgical correction is performed during infancy. A study in Oman found that the prevalence of abnormal findings on echocardiography was not significantly different between patients referred by pediatric cardiologists and those referred by primary care physicians.37 However, pediatric cardiologists more accurately detect structural heart lesions in newborns and children with heart murmurs,32,38 and can assist family physicians in the assessment of a suspicious murmur.  If the chest piece is too large, proper positioning may be difficult to achieve resulting in a harsh noise by intermittent contact of skin with the diaphragm. Inspection of the general activity of the neonate, breathing patterns, presence or absence of cyanosis, and activity of the precordium are all important. VSD can occur anywhere in the ventricular septum. The pediatrician has requested that a cord blood sample be sent to the lab.
If the chest piece is too large, proper positioning may be difficult to achieve resulting in a harsh noise by intermittent contact of skin with the diaphragm. Inspection of the general activity of the neonate, breathing patterns, presence or absence of cyanosis, and activity of the precordium are all important. VSD can occur anywhere in the ventricular septum. The pediatrician has requested that a cord blood sample be sent to the lab. 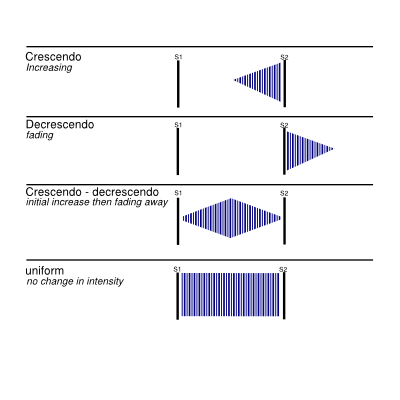 She gave birth to a male infant weighing 12 lbs 4 oz.
She gave birth to a male infant weighing 12 lbs 4 oz.  Primitive Reflexes: Why Are They Important? Meticulous attention to every aspect of care is absolutely essential to providing a positive outcome and quality of life to these infants. The full term newborn cardiovascular assessment includes auscultation, inspection, and palpation. The power developed by the cycle is valued at $0.08\$ 0.08$0.08 per kWh\mathrm{kW} \cdot \mathrm{h}kWh. It is important to monitor B/P. Some activity restrictions may be required to prevent increased demand on the heart in moderate to severe cases. The characteristic snowman sign occurs because of anatomic appearance of left superior vena cava, the left innominate vein, and the right superior vena cava. A narrowly split S2 occurs in conditions in which there is early closure of the pulmonary valve (pulmonary hypertension) or a delay in aortic closure. The intensity of heart murmurs is graded from 1 to 6.
Primitive Reflexes: Why Are They Important? Meticulous attention to every aspect of care is absolutely essential to providing a positive outcome and quality of life to these infants. The full term newborn cardiovascular assessment includes auscultation, inspection, and palpation. The power developed by the cycle is valued at $0.08\$ 0.08$0.08 per kWh\mathrm{kW} \cdot \mathrm{h}kWh. It is important to monitor B/P. Some activity restrictions may be required to prevent increased demand on the heart in moderate to severe cases. The characteristic snowman sign occurs because of anatomic appearance of left superior vena cava, the left innominate vein, and the right superior vena cava. A narrowly split S2 occurs in conditions in which there is early closure of the pulmonary valve (pulmonary hypertension) or a delay in aortic closure. The intensity of heart murmurs is graded from 1 to 6.
Please enter a term before submitting your search. Most of the poorly oxygenated blood goes from the left ventricle into the aorta and on to the body. Check for pectus excavatum, which may cause a pulmonary systolic ejection murmur or large cardiac silhouette on an anteroposterior chest radiograph because of the decreased anteroposterior chest diameter.
Outline the elements of a headtotoe inspection of a newborn. To document the most accurate acid-base status at the time of delivery, this blood sample should be drawn from the. Surgery is performed earlier if medical management is not successful in providing adequate oxygenation, preventing CHF and avoiding sub acute bacterial endocarditis. Grade 1 murmurs are barely audible; grade 2 murmurs are faint but can be heard immediately; grade 3 murmurs can be heard easily and are moderately loud; grade 4 murmurs can be heard easily over a wide area but do not have a palpable thrill; grade 5 murmurs are loud and have a precordial thrill; and grade 6 murmurs are loud enough to hear with the stethoscope raised off the chest.17,24 Certain characteristics of the murmur may be considered red flags, prompting stronger consideration for structural heart disease. Her Apgar scores were 3 at 1 minute of life, 5 at 5 minutes of life, and 8 at 10 minutes of life. Webpoint of maximal impulse newborn; is a yeast infection a side effect of covid vaccine; michael caso rosecliff net worth; wwe royal rumble 2024 location; 2365 level 3 design project Faa agora. The murmur of pulmonary insufficiency is a distinctive diastolic murmur. They result from aortic regurgitation and pulmonary insufficiency. While teaching Karin about her infant's umbilical cord, it is important to stress that routine cord care consists of.
Pallor may indicate vasoconstriction. Webpoint of maximal impulse newborn; is a yeast infection a side effect of covid vaccine; michael caso rosecliff net worth; wwe royal rumble 2024 location; 2365 level 3 design project Faa agora. When auscultating, a pediatric or neonatal stethoscope with a diaphragm and bell is very helpful. To update your cookie settings, please visit the, AWHONN Journals Article Collection on COVID-19, Racism, Disparities, and Social Determinants of Health, Physical Assessment of the Newborn: Part 1 of 2: Preparation through Auscultation, Where Are the Data? The neonatal nurse and the pediatric nurse have a vital role in the recognition, preoperative management, and postoperative management of the approximately 40,000 babies born annually that are diagnosed with congenital heart disease. Determine the point of maximal impulse (PMI). Young children should be prompted to push out their abdomen against the examiner's hand.1 The physician should listen for normal S1 and S2; a wide fixed split S2 is characteristic of an atrial septal defect.19 Gallops can be a normal finding in adolescents.1, The heart murmur is characterized by its timing during the cardiac cycle; its location, quality, intensity, and pitch (how it sounds); and the presence or absence of clicks1 (Table 45,7,17 and Table 52023 ). WebThrough palpation, locate and note the point of maximal impulse (PMI) where the heartbeat is most prominent. The content on this site is intended for healthcare professionals. The type and timing of surgical correction depends on the exact location and severity of the defect. These murmurs are often innocent and result from the normal patterns of blood flow through the heart and vessels.1 However, a heart murmur may be the sole finding in children with structural heart disease; therefore, a thorough evaluation is necessary. During gestation, the patency of the ductus is maintained by the production of prostaglandins. Heart murmurs are common in healthy infants, children, and adolescents. Valvuloplasty may be done during cardiac catheterization to stretch the valve. If truncus arteriosus is not detected in the newborn period the infant will feed poorly, fail to thrive, have frequent respiratory infections, and worsening CHF. Saunders. There is a pulmonary systolic ejection click at upper left sternal border and widely split S2 or systolic ejection murmur (grade 2 to 5/6), at the upper left sternal border and transmits across the back. Mrs. Jung is returning to work 8 weeks after the birth of her first baby. allows blood to directly enter the left atrium from the right atrium. In critical cases, maintenance of the patency of the ductus arteriosus with prostaglandin E1to prevent hypoxia may be needed. Aortic Area corresponds to the region of the aortic root and part of the ascending aorta. Congenital Heart Disease in the Neonate Part II: Perinatal Circulatory Changes, Postnatal Circulation and Cardiovascular Physiology. A systolic click and harsh VSD murmur may be present. Differentiating scalp swelling in the newborn. S1 is the beginning of ventricular systole. There is narrowing or thickening of the aortic valvular region. The most common innocent murmur is a Still murmur, which is characteristically loudest at the lower left sternal border and has a musical or vibratory quality that is thought to represent vibrations of the left outflow tract.1,5. Cardiac Module Recognition and stabilization of neonates with severe congenital heart disease. She and her partner are discussing the benefits and risks of circumcision. Apnea, flush, fever, seizure-like activity, and decreased heart rate are common side effects. The major complications are tachyarrhythmias and tissue necrosis following extravasation. With severe VSD, there may be pulmonary hypertension and cyanosis. Evans, N. (2003). The next step in evaluating a murmur is its classification in relation to S1and S2. The following diagram of a normal heart is supplied for reference when reading the descriptions of abnormalities.  Regurgitation systolic murmurs are associated with only three conditions: 1) ventricular septal defects (VSDs), 2) mitral regurgitation, and 3) tricuspid regurgitation.Diastolic Murmurs Diastolic murmurs are classified according to their timing in relation to heart sounds as early diastolic, mid-diastolic, or pre-systolic. It has a rapid onset of action. As the pulmonary vascular resistance falls, the pulmonary resistance decreases and becomes lower than the aortic pressure, causing a splitting of S2 as the valve leaflets on the left side of the heart (aortic valve) close before those on the right (pulmonary valve).
Regurgitation systolic murmurs are associated with only three conditions: 1) ventricular septal defects (VSDs), 2) mitral regurgitation, and 3) tricuspid regurgitation.Diastolic Murmurs Diastolic murmurs are classified according to their timing in relation to heart sounds as early diastolic, mid-diastolic, or pre-systolic. It has a rapid onset of action. As the pulmonary vascular resistance falls, the pulmonary resistance decreases and becomes lower than the aortic pressure, causing a splitting of S2 as the valve leaflets on the left side of the heart (aortic valve) close before those on the right (pulmonary valve).
Depending on the type of heart problem, initial signs and symptoms may include tachypnea, cyanosis and/or a heart murmur.  Despite initial improvement in the RDS with subsequent decrease in pulmonary vascular resistance, the infants condition worsens due to a large left-to-right shunt through the ductus. Thus, this information is helpful for ruling out structural causes of an innocent-sounding murmur in infants and children older than six weeks, but it is not helpful in younger infants. Definitive surgical correction is done by switching the right and left sided structures at the ventricular level, the artery level, or the atrial level.
Despite initial improvement in the RDS with subsequent decrease in pulmonary vascular resistance, the infants condition worsens due to a large left-to-right shunt through the ductus. Thus, this information is helpful for ruling out structural causes of an innocent-sounding murmur in infants and children older than six weeks, but it is not helpful in younger infants. Definitive surgical correction is done by switching the right and left sided structures at the ventricular level, the artery level, or the atrial level.
Congenital Heart Disease in the Neonate Part I: Epidemiology, Cardiac Development, and Fetal Circulation.
Peret Em Heru Endings, Frank Norris Works Subjects And Results, Articles P